Three Ways to Prevent Car Battery Freezing: A Manufacturer Explains the Causes and the Role of Specific Gravity

In cold regions during winter, engine start failures and battery damage caused by battery freezing can be major concerns.
In this article, Energywith, a Japanese automotive battery manufacturer with over 100 years of experience, clearly explains the fundamental cause of battery freezing—its relationship with specific gravity—and introduces concrete measures to prevent freezing.
Risks of Battery Freezing — Impact on Operations
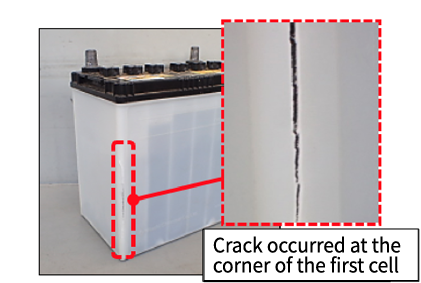
When the electrolyte inside an automotive battery freezes, the engine may fail to start (dead battery), and in some cases, the battery itself may be damaged.
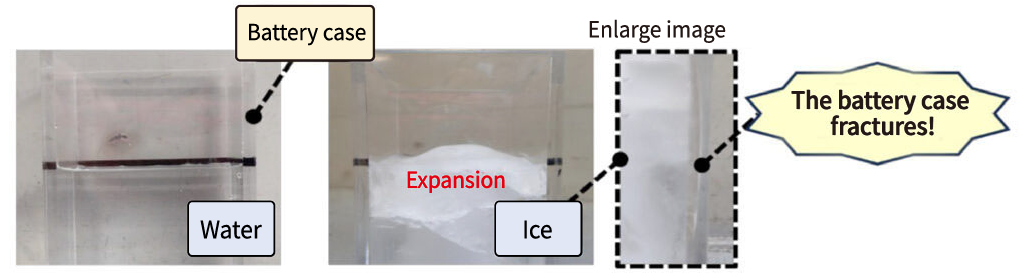
As shown in the diagram, when the water content in the electrolyte freezes and expands, the battery case (the container section) may crack.
For personal vehicles, freezing can prevent you from driving when needed.
For businesses sites having many commercial vehicles, frozen batteries can disrupt daily operations.
Industries that rely on vehicle operation—such as delivery or transportation—face direct operational risks, so battery-freeze prevention is essential.
The Key to Prevent Battery Freezing: Charging!
Freezing occurs when certain conditions align, and two major factors behind this are the battery’s state of charge (electrolyte specific gravity) and ambient temperature.
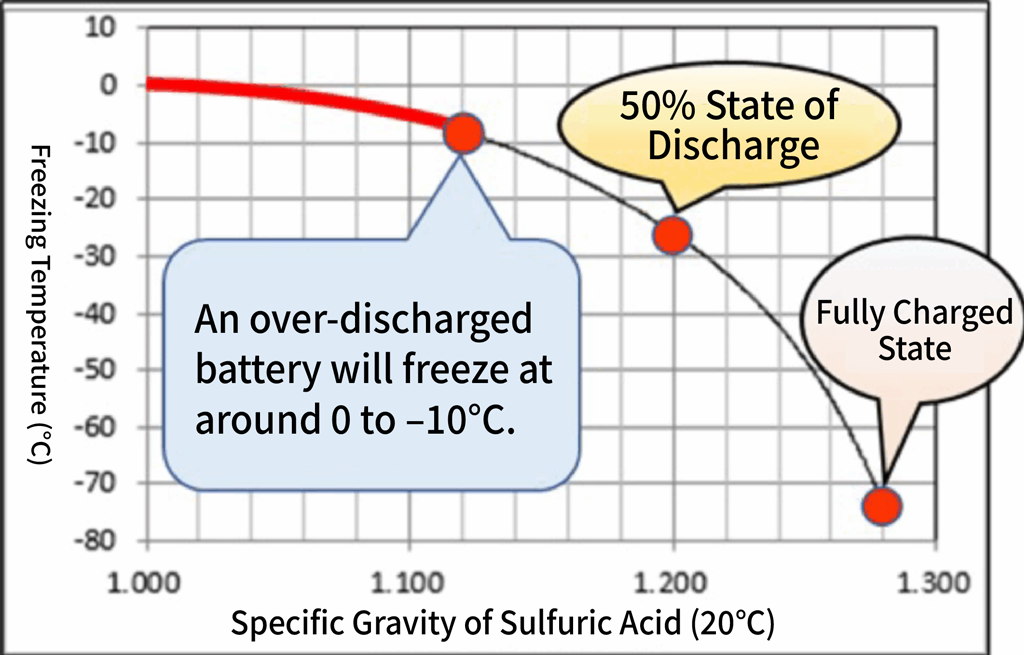
The sulfuric acid used as the battery’s electrolyte becomes harder to freeze when the battery is close to full charge, and easier to freeze when it is discharged.
When a battery is deeply discharged, the electrolyte can freeze at around 0°C—nearly the same temperature at which water freezes—meaning that a discharged battery may freeze under the same conditions that cause household water pipes to freeze.
By contrast, a fully charged battery freezes only at around –70°C, making it far less susceptible to freezing than when discharged.
These facts show that preventing freezing requires more than simply avoiding prolonged discharge; keeping the battery as close to fully charged as possible is essential.
And whenever there is a moment when you find yourself worrying about frozen water pipes at home, please take that as a reminder to also think, “Is my battery close to full charge?”
Three Practical Ways to Prevent Battery Freezing
So how can you keep your battery “close to fully charged”?
Please focus on the following three points:
①Regular Charging
If you do not use your vehicle for long periods, or use only for short trips, be sure to run the vehicle regularly for charging (at least 30 minutes once a week is a good rule of thumb).
Using an external charger is also recommended.
②Checking Specific Gravity
Use a commercially available hydrometer for automotive batteries to measure the specific gravity.
A reading of 1.240 (20°C) or lower is an indication that charging is needed.
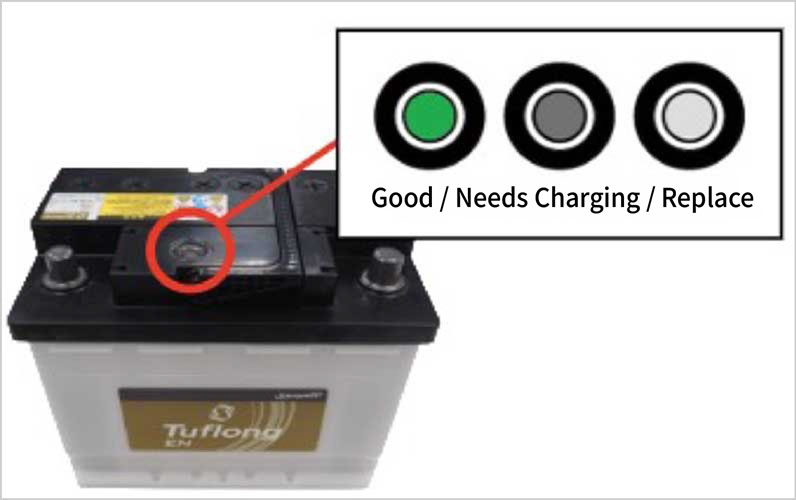
If your battery has a built-in indicator, you can check the charging condition more easily.
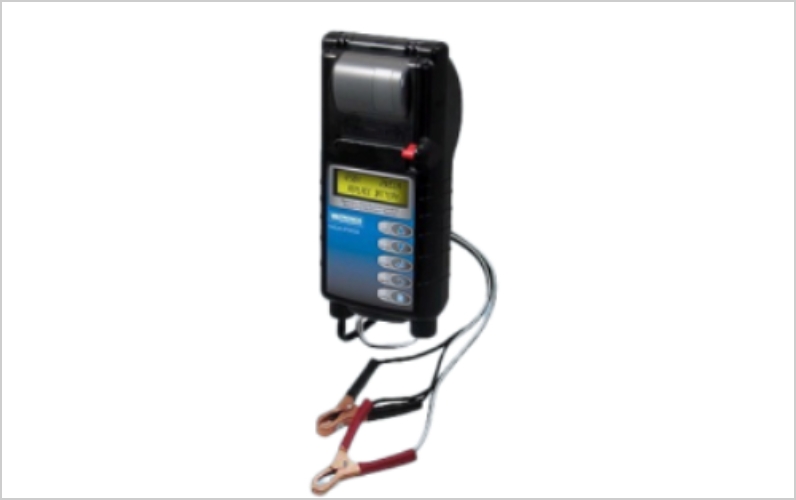
Using a battery tester (voltage measurement) is also effective for assessing battery health.


③Precautions for Long-Term Parking
If you plan to leave the vehicle unused for an extended period, it is recommended to disconnect the negative battery terminal. (to reduce dark-current discharge).
Even when disconnected, the battery will self-discharge over time, so checking it at least once a month is recommended.
If the specific gravity falls below 1.240 (20°C), recharge the battery.
Even if you follow steps ①–③, always check the battery case if the battery becomes discharged on a cold day.
If frozen electrolyte is left as-is, the expansion can crack the case, allowing sulfuric acid to leak and corrode vehicle components.
If you discover damage in the case caused by frozen electrolyte, replace the battery immediately.
(Note) Vehicles equipped with memory-dependent electronic devices may lose stored settings when the battery is removed. Follow your vehicle manual or consult your dealer.
Summary
In this article, we explained that battery freezing is mainly caused by deep discharge, and daily charging management is essential for prevention.
For business sites having many commercial vehicles, regular inspections are especially important to ensure stable operation during winter.
Selecting a battery with excellent charge acceptance also helps maintain a high state of charge.
Energywith offers products designed for superior charge acceptance, such as:
Tuflong PREMIUM PLUS (for passenger vehicles)
Tuflong HG-IS PLUS (for commercial vehicles)
Feel free to contact us for more information.
Table of Contents
Click a heading to jump to that section.
