Virtual Factory Tour (Saitama Works)
Products Manufactured
Factory Facilities Overview

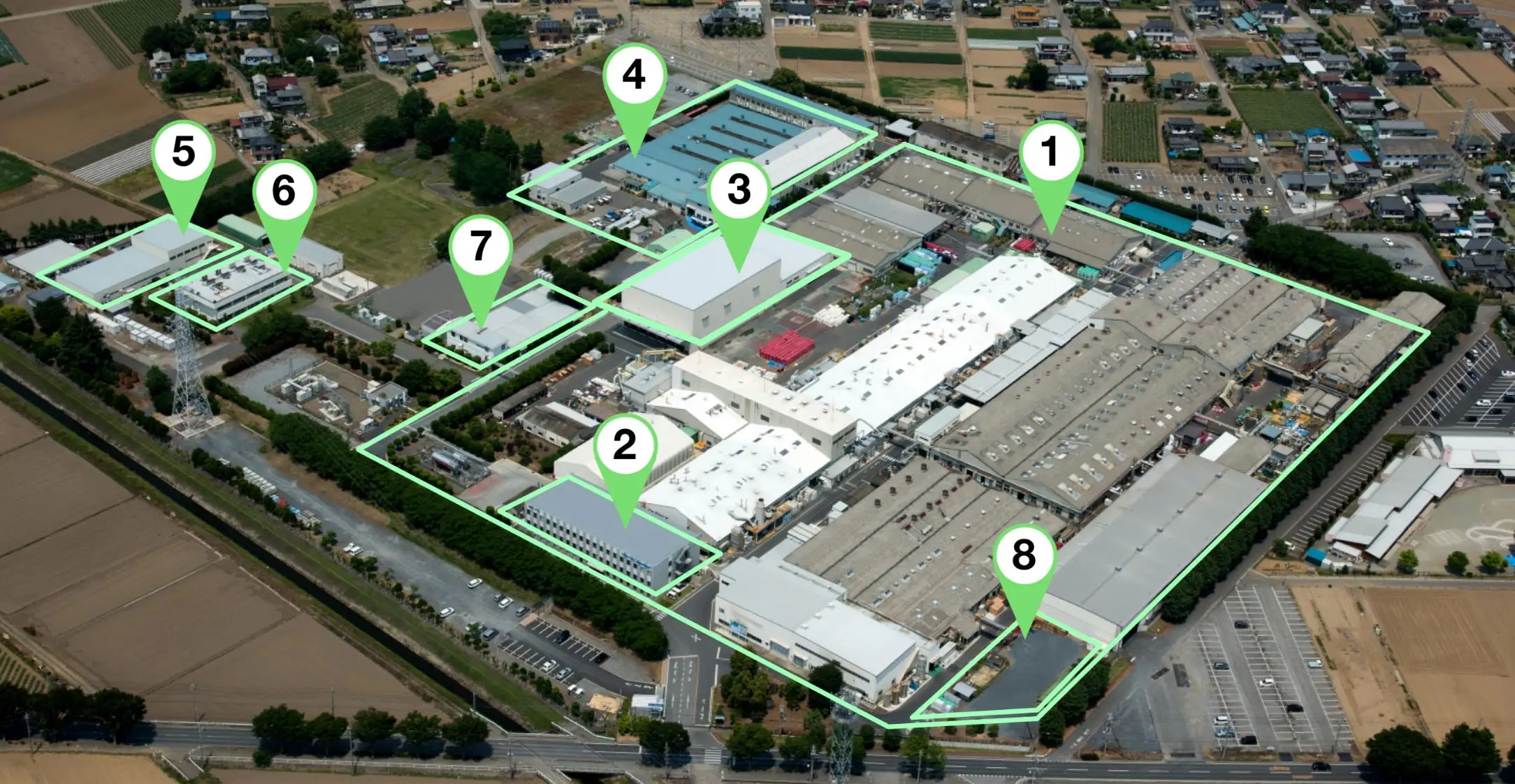
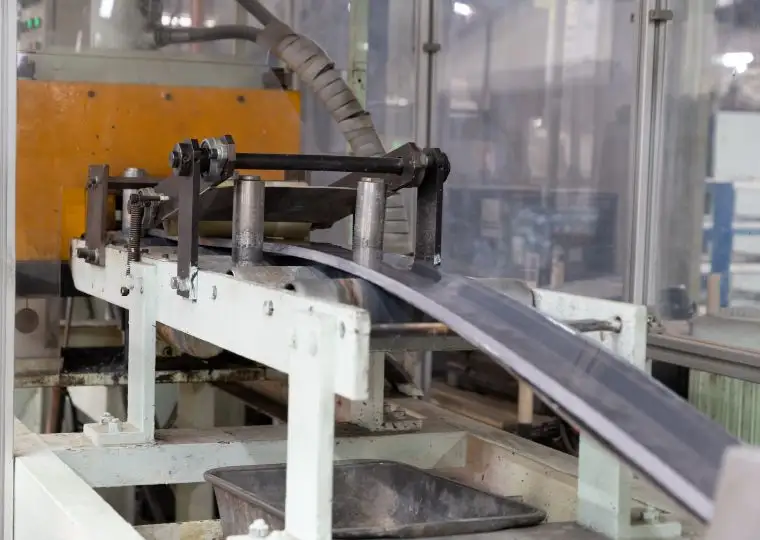
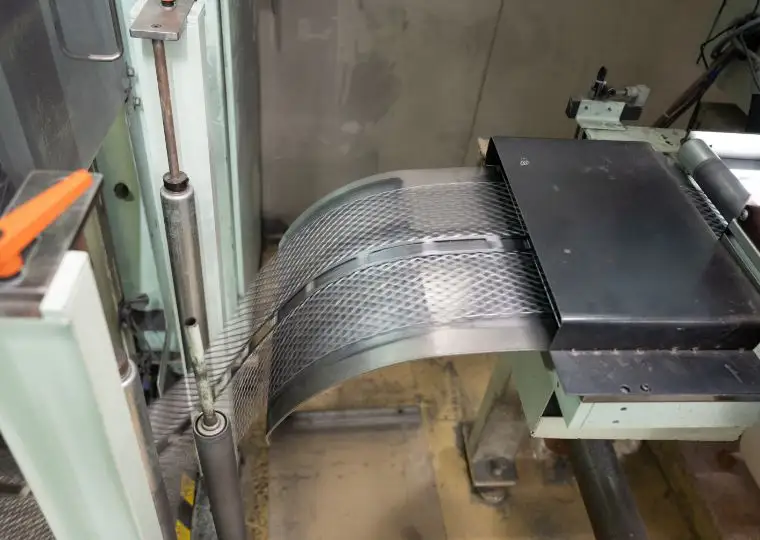
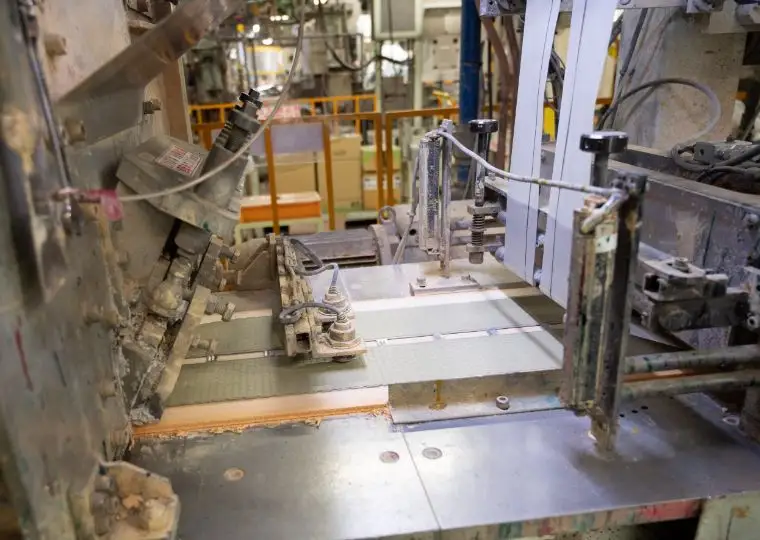
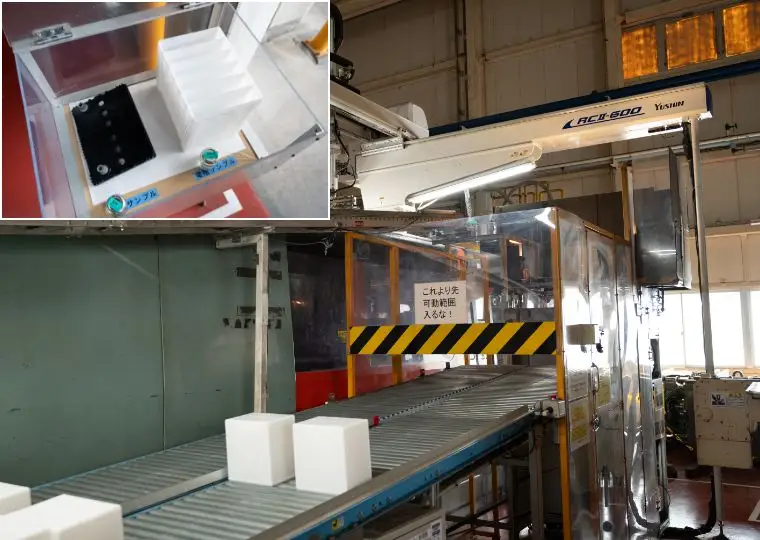
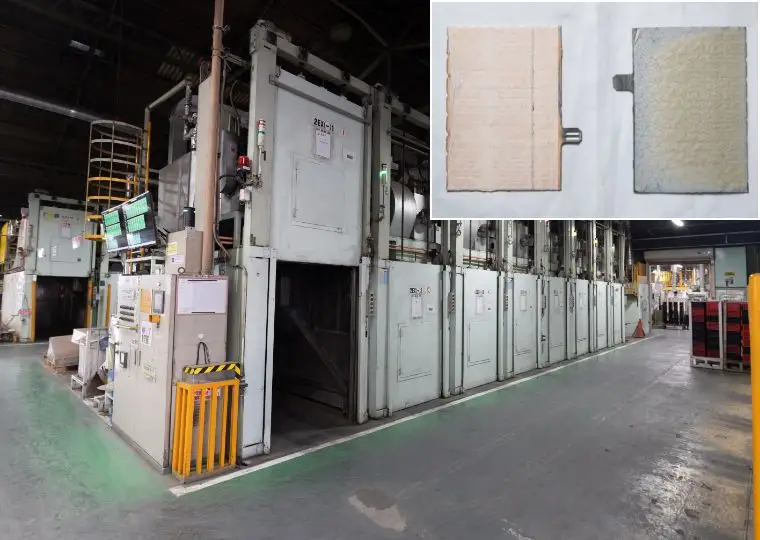
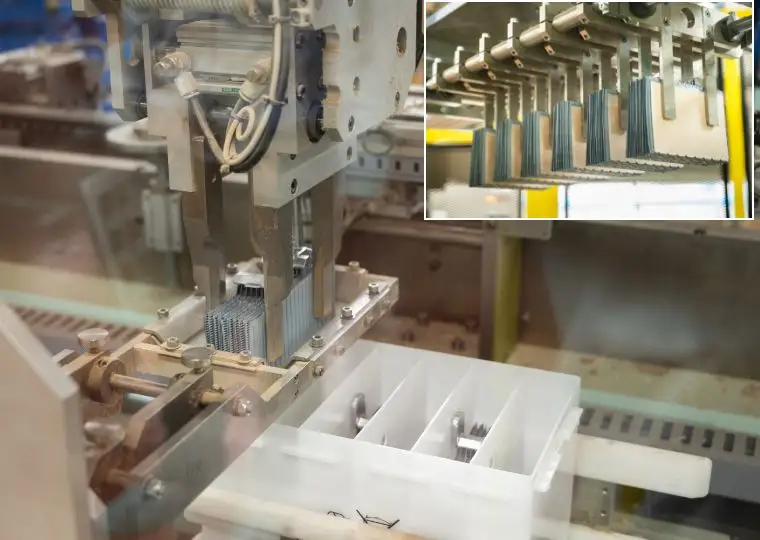
Battery Plant (Automotive Battery Manufacturing)
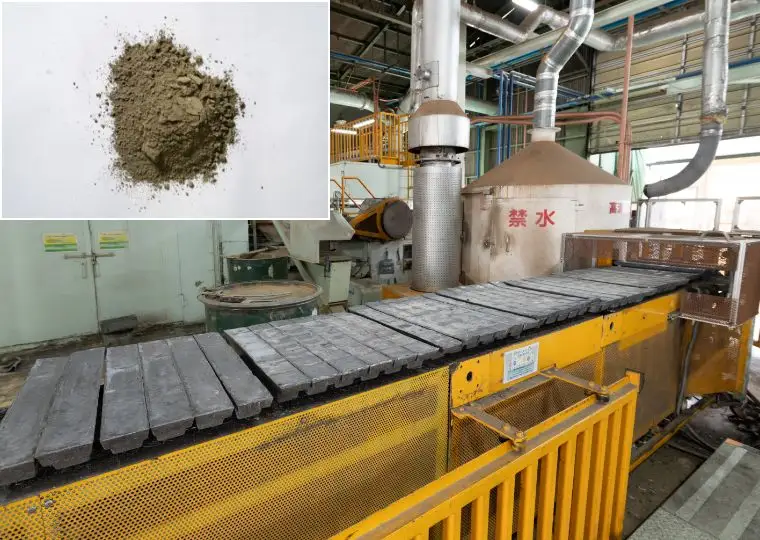
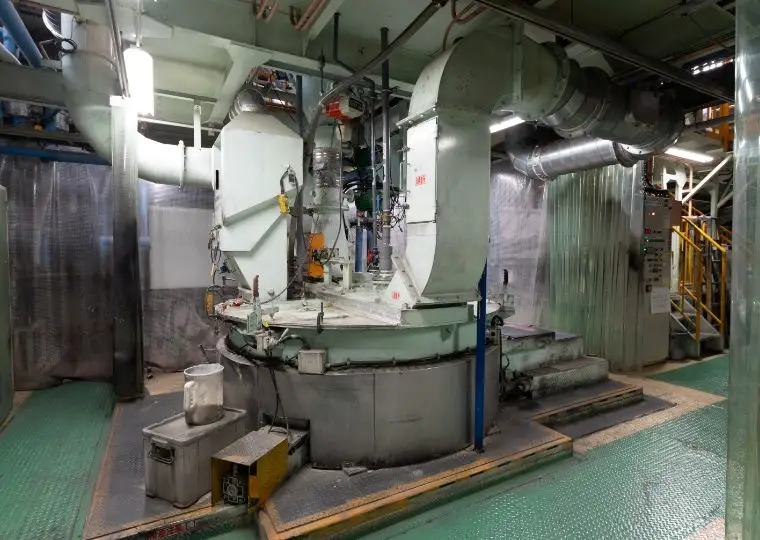
This plant is equipped with all processes required to manufacture automotive lead acid batteries—ranging from raw materials and electrode plate production to assembly, charging, and packaging. It produces batteries for a wide variety of applications, including passenger cars, buses, trucks, agricultural machinery, and construction machinery.

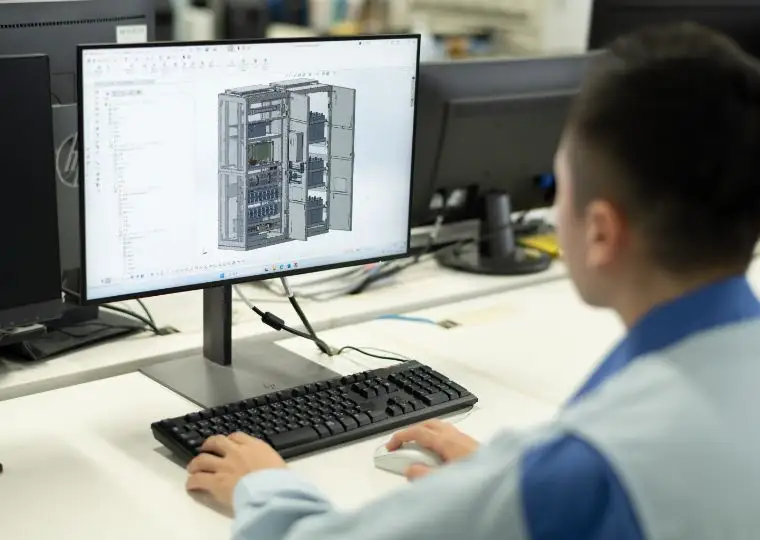
Technology & Administration Building
This building houses technical departments such as design, quality assurance, and environmental safety, as well as administrative divisions including HR & General Affairs, Finance, IT, and Procurement. It plays a critical role in supporting the overall functions of the site by integrating technical and administrative capabilities.

Automated Warehouse
A large automated warehouse capable of storing up to 6,000 pallets (approx. 300,000 automotive batteries). Automotive batteries produced at the plant are shipped from here to destinations across Japan.

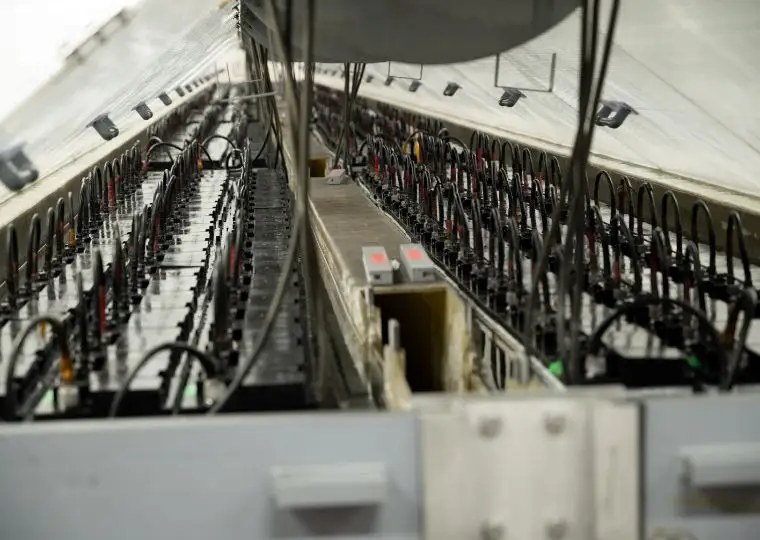
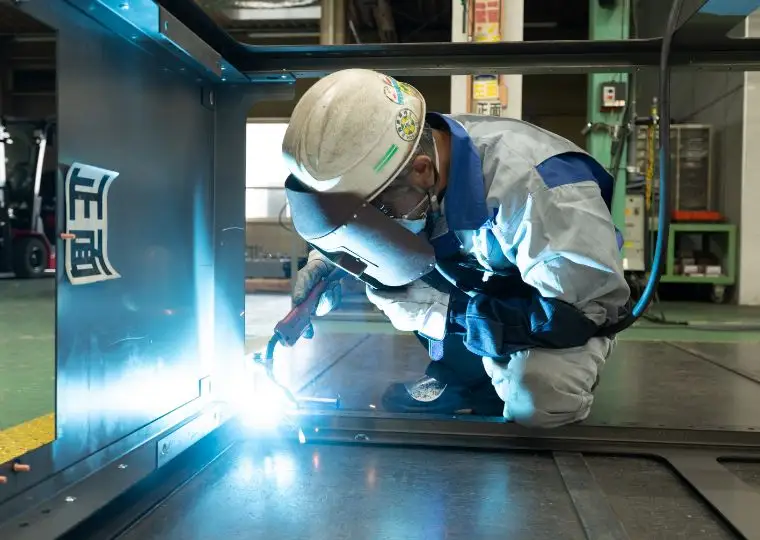
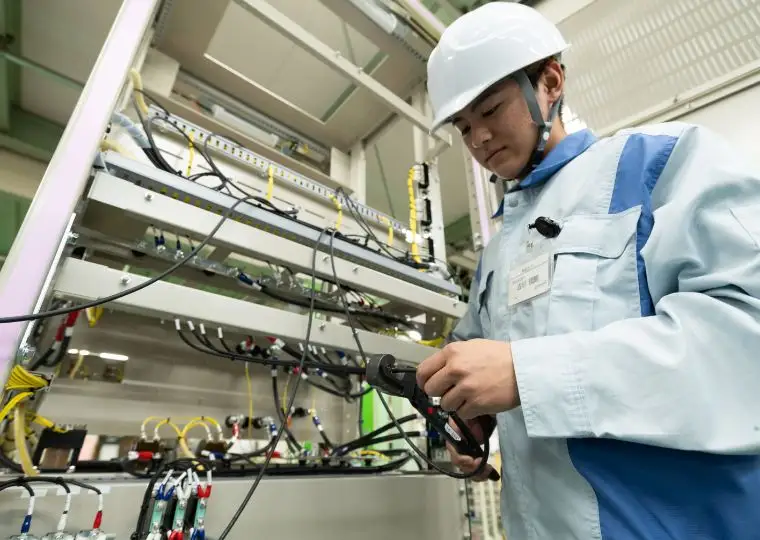
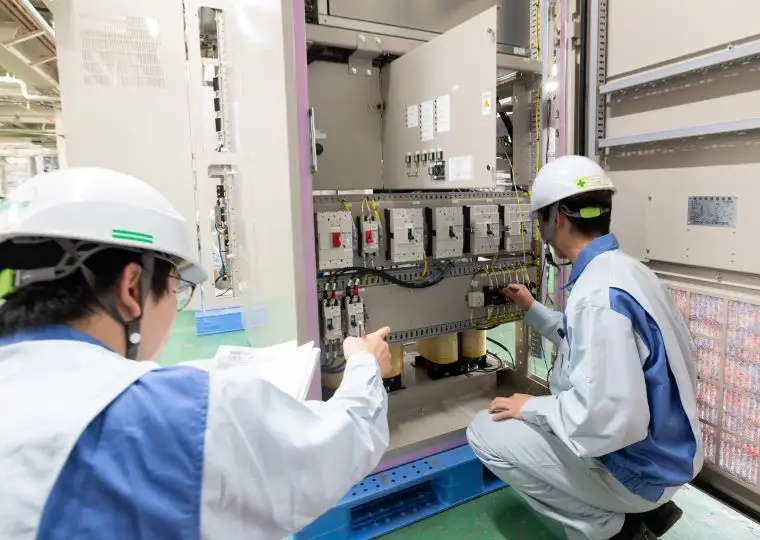
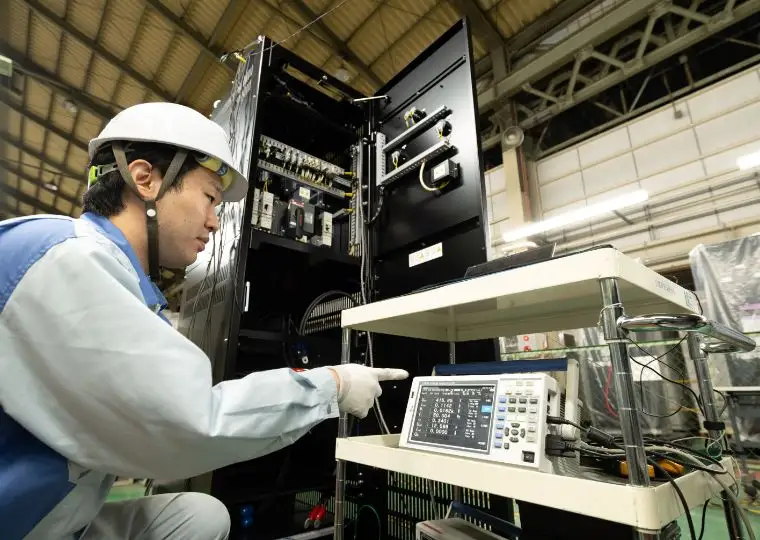
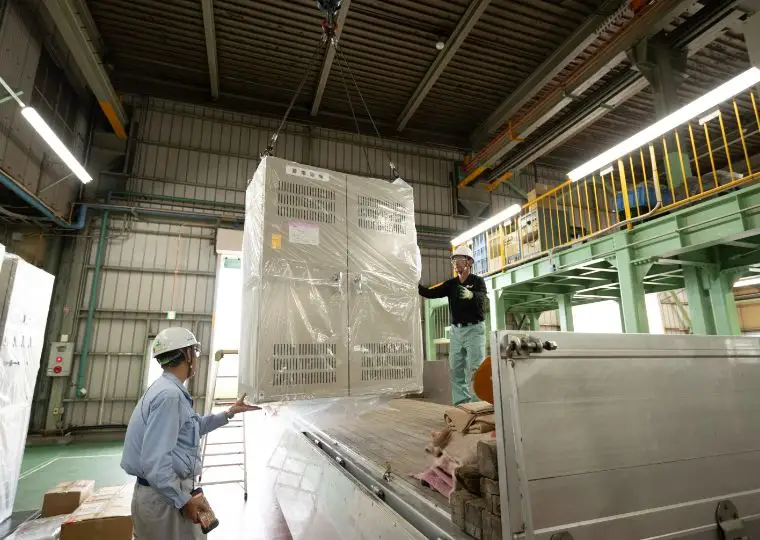
Equipment Plant
This plant handles everything from sheet-metal processing to cabinet fabrication, assembly, wiring, performance testing, and final shipment for DC power supply equipment. These units ensure stable power supply to equipment that must remain operational during power outages or for control systems, making them indispensable devices combined with storage batteries.
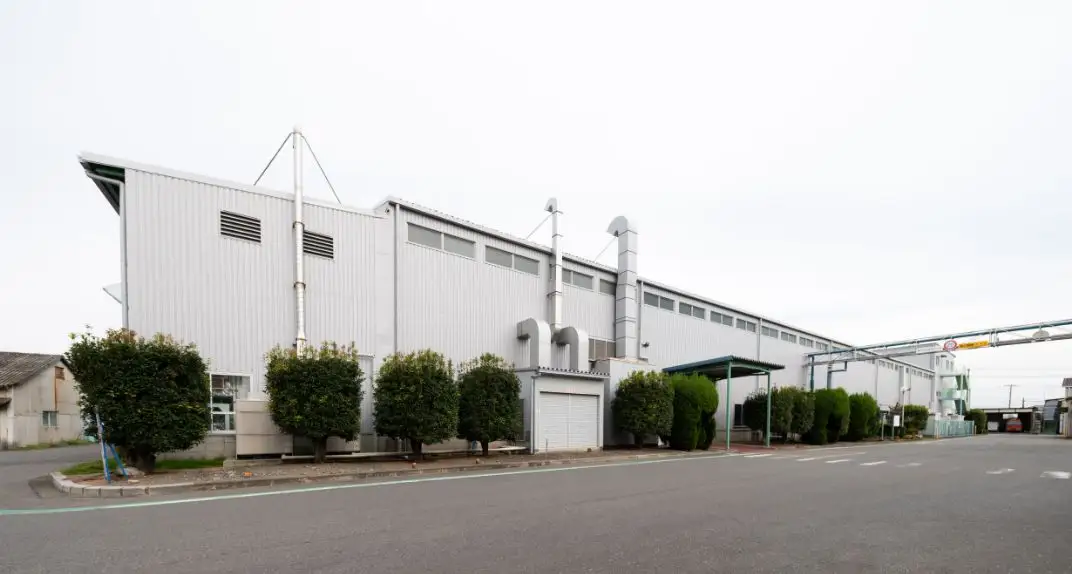

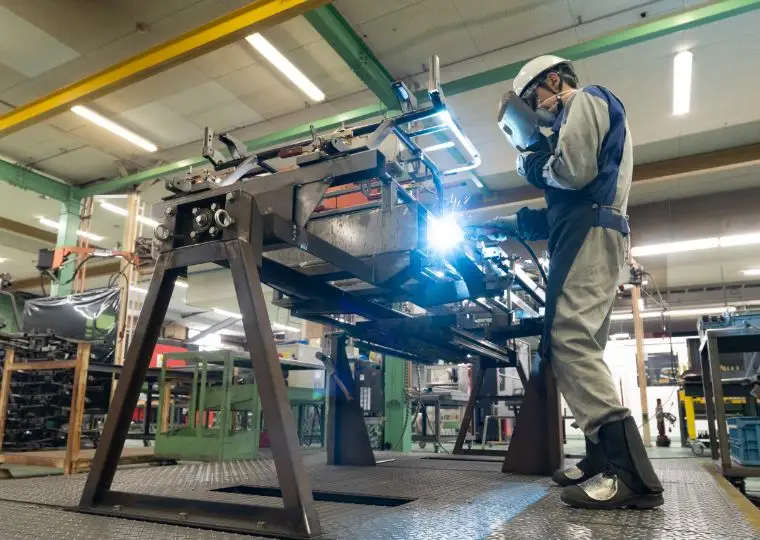
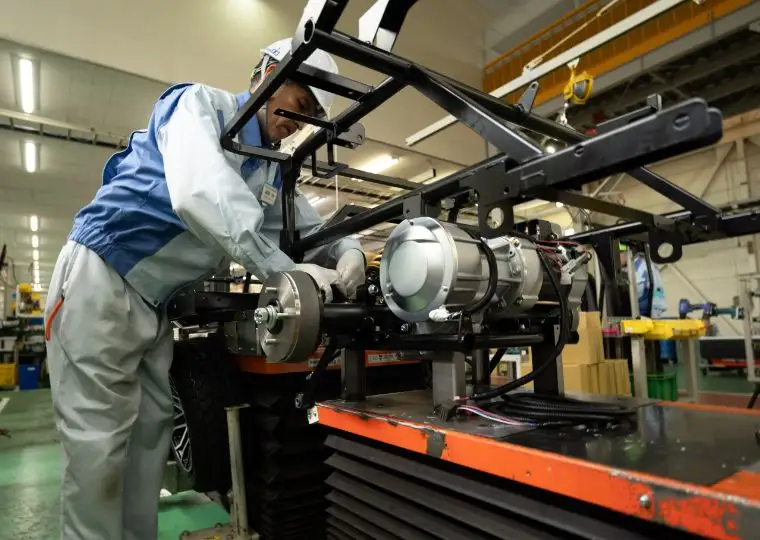
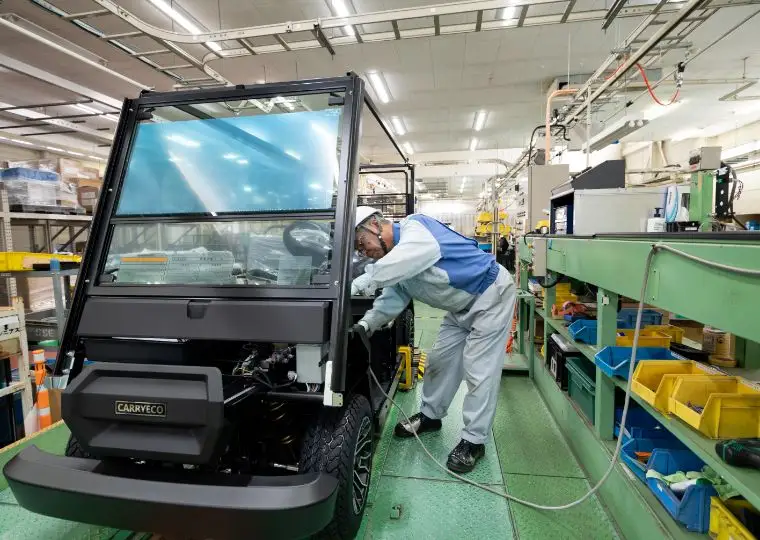
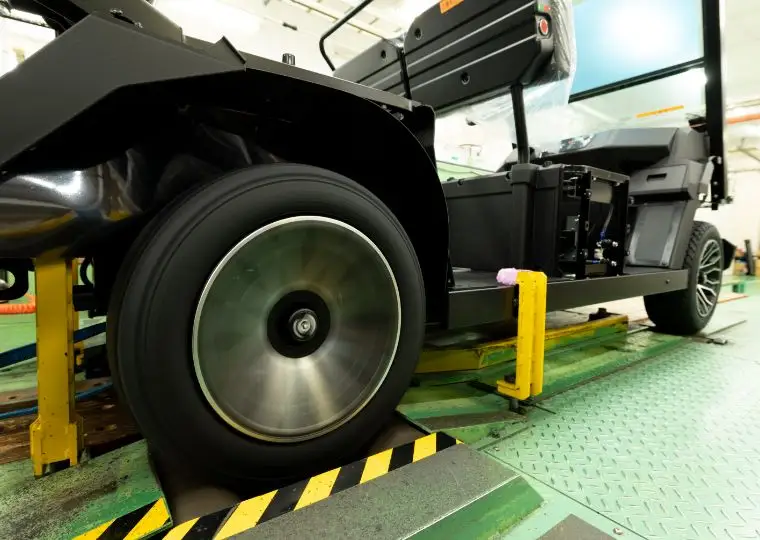
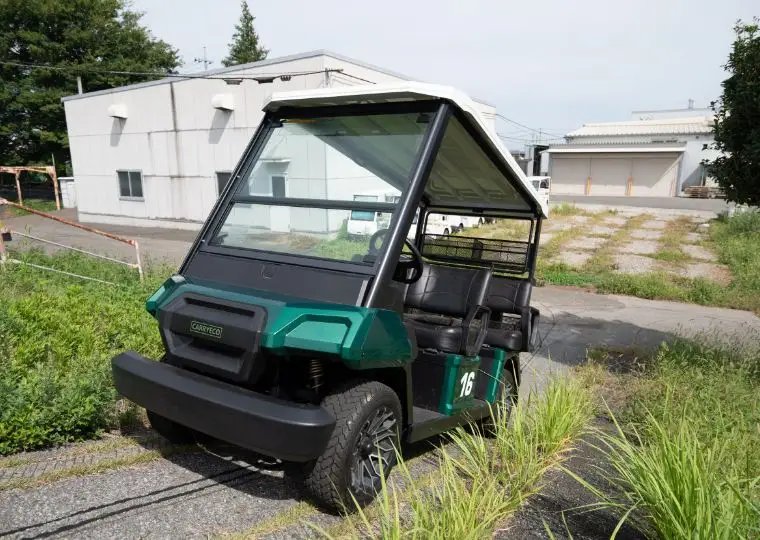
Cart Plant
Energywith is the first company in Japan that developed electric carts. This plant manufactures electric carts used not only at golf courses but also in tourist areas, factories, and resort facilities.
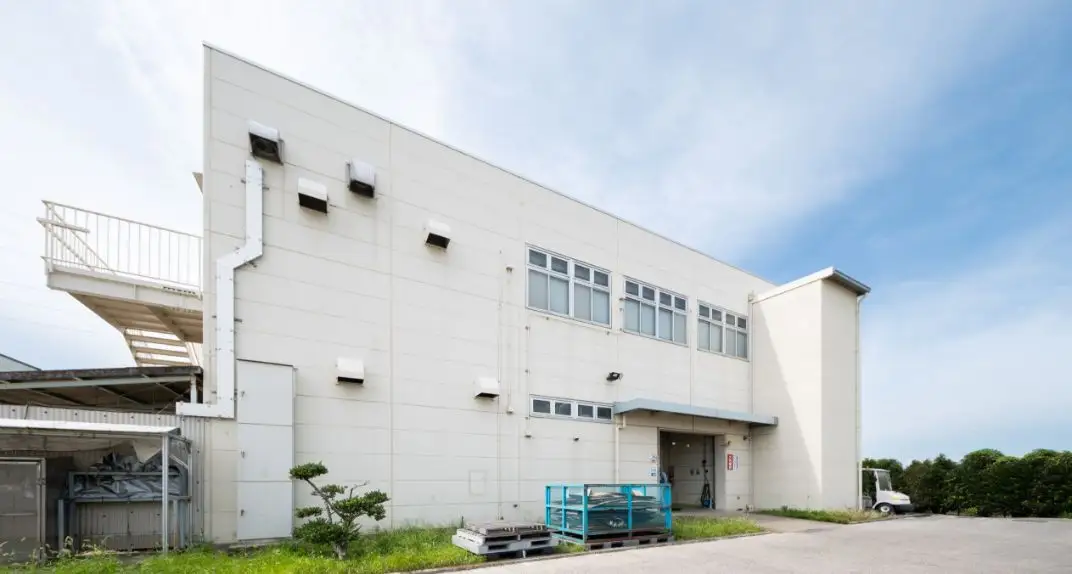

Research Building
Energywith is responsible for developing elemental technologies that enhance the performance of lead acid batteries, as well as conducting R&D for promising nickel-zinc batteries and next-generation batteries.

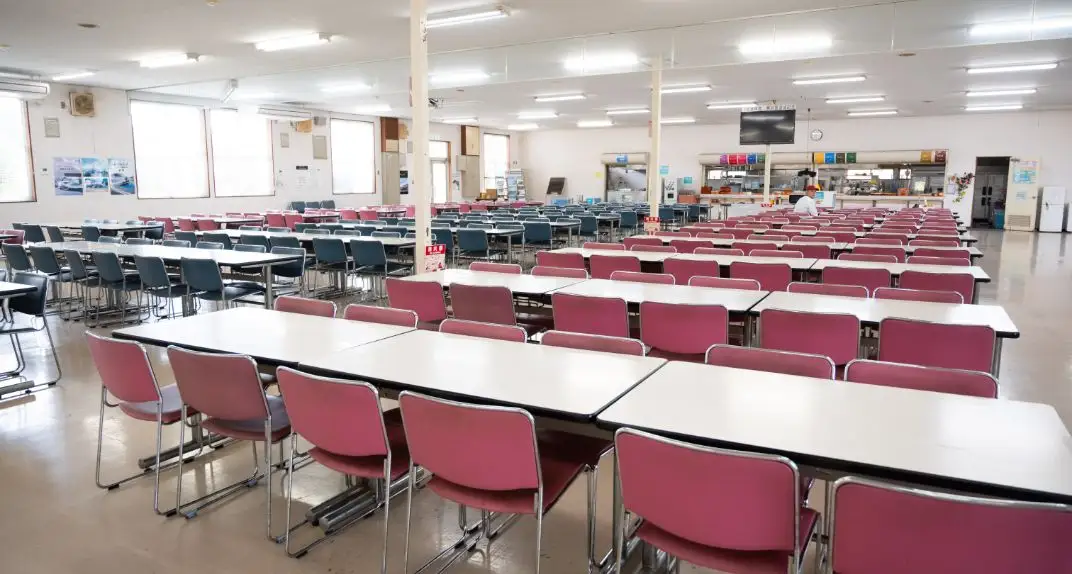
Cafeteria
The employee cafeteria offers a bright and clean dining space with nutritious daily menus at reasonable prices—serving as a place of relaxation that supports both the body and mind of employees.

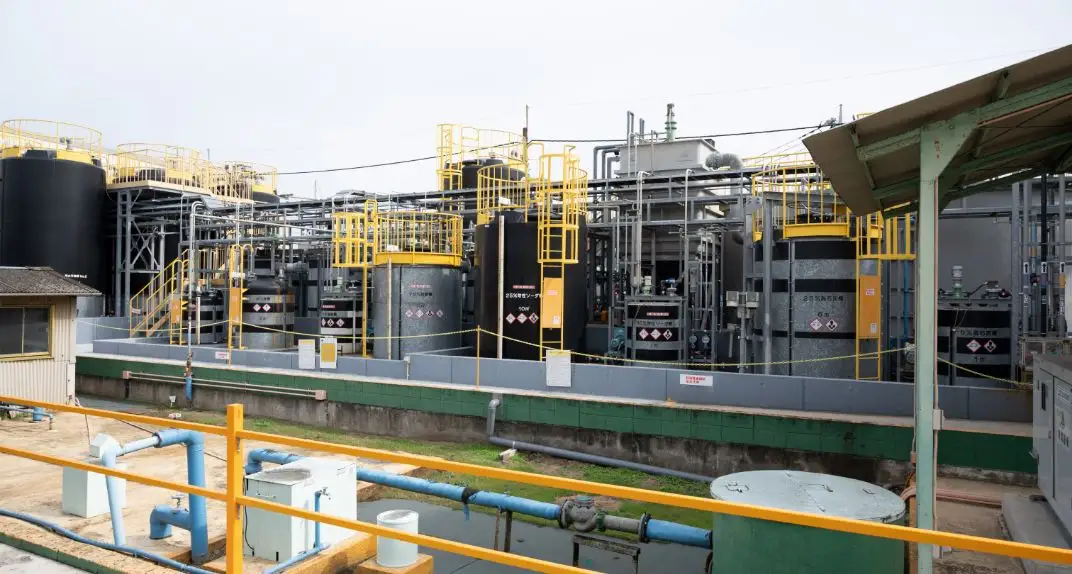
Water Treatment Plant
This facility reduces lead content and acidity in wastewater generated from various manufacturing processes to below environmental regulatory levels, enabling safe discharge into rivers. It plays a key role in minimizing environmental impact.